I think one of the most exciting developments in the author world is the advancement of AI.
True, there are many unknowns with AI as well, but one development that provides a lot of potential for authors is AI art.
AI art has taken huge leaps forward, to the point that it is now a highly useful tool for authors.
But there are many questions still unanswered, such as copyright, which program you should use, etc. And so I have written this article to clear up any confusion.
- Which AI art generator you should use
- The situation around AI art copyright
- The best use cases for authors
Table of contents
My Litmus Test
When testing out different AI art tools, I like to have a litmus test to help judge how effective it is. To do this, I pick a prompt that is intentionally complicated.
One of the litmus tests I have used frequently is generating Egyptian gods. Why Egyptian gods? Because they are a combination of human features and animal features, which is something that AI art often struggles to do.
Also I’m an amateur mythologist.
So for many of the examples in this article, I will be using this prompt:
“The egyptian god Ra, head of a falcon, superhero pose, desert background, epic, powerful, concept art style”
Don't worry, I will explain the logic of writing your prompts later in this article.
Better Keywords & Categories Fast
See why over 47,000+ authors and publishing companies use and love Rocket to help them sell more books.
Get Publisher Rocket Now!The Top Four AI Art Generators
There are literally dozens of AI art tools out there, and many have their own unique specialty. But for authors, there are a few that stand out the most:
- Midjourney
- Dall-E
- Stable Diffusion
- Ideogram
Additionally, if you'd like to know more about how author can leverage AI, I'd invite you to check out my Story Hacker community, where we have dedicated teachers on various topics, including AI art.
1. Midjourney
Of all the AI tools out there, Midjourney is my top recommendation for authors, and for most artists in general.
In the past year, Midjourney has gone from okay to absolutely incredible.
Ever since the release of version 4 in late 2022, Midjourney surpassed every other AI tool both in the beauty of its artwork, and in the accuracy of its subjects. And it's now gone far above version 4.
But don't take my word for it, see what it generated with my litmus test prompt (this was generated with version 6.1):

How Much Does Midjourney Cost
Midjourney has three pricing tiers:
- $10/month (200 mins of GPU time)
- $30/month (15 hrs of GPU time)
- $60/month (30 hrs of GPU time, plus stealth mode)
- $120/month (60 hrs of GPU time, plus stealth mode)
If you use AI art a lot, you'll definitely want at least the $30 option, because you will soon find that you can burn through 200 mins of GPU time very quickly. But for those just curious to dabble, the $10/month tier is just fine.
The nature of AI art means that you are constantly running your prompt over and over again to try and get something closer to what you want, or simply because you enjoy experimenting.
Trust me, it can get addictive real fast. The fact that Midjourney has, essentially, unlimited generations at their upper tiers is a huge plus.
Side note: Midjourney also has a “privacy” plan for the $60 and above plans, which lets you generate images that WON'T be visible to others in the Midjourney community. This is useful if you don't want people to know exactly where the images come from.
Why I recommend Midjourney for authors:
- Accuracy: It is by far the most accurate tool for most prompts. You are much more likely to get what you want.
- Artistry: I believe the majority of the images Midjourney creates are much more artistic and beautiful than any of its competitors.
- Community: Midjourney has a thriving community, and it can be a lot of fun to browse other people's creations and try the same prompts yourself.
- Cost: Midjourney essentially lets you generate unlimited images with its upper pricing tiers. And it's only $30 a month or more. An unlimited pricing tier is essential, because you will find yourself running these problems over and over again to get exactly what you want.
You can access Midjourney over on their website: https://www.midjourney.com/
2. Dall-E
Dall-E is another AI art generator that, while not quite on the same level as Midjourney (at least as of this writing), is still a favorite because it is directly integrated into ChatGPT.
Dall-E does have a couple of unique features that make it better in some use cases, such as the ability to chat directly with ChatGPT to ask for revisions, but overall I still recommend Midjourney as the best AI art tool for authors.
Let's take a look at how it does with my litmus test:
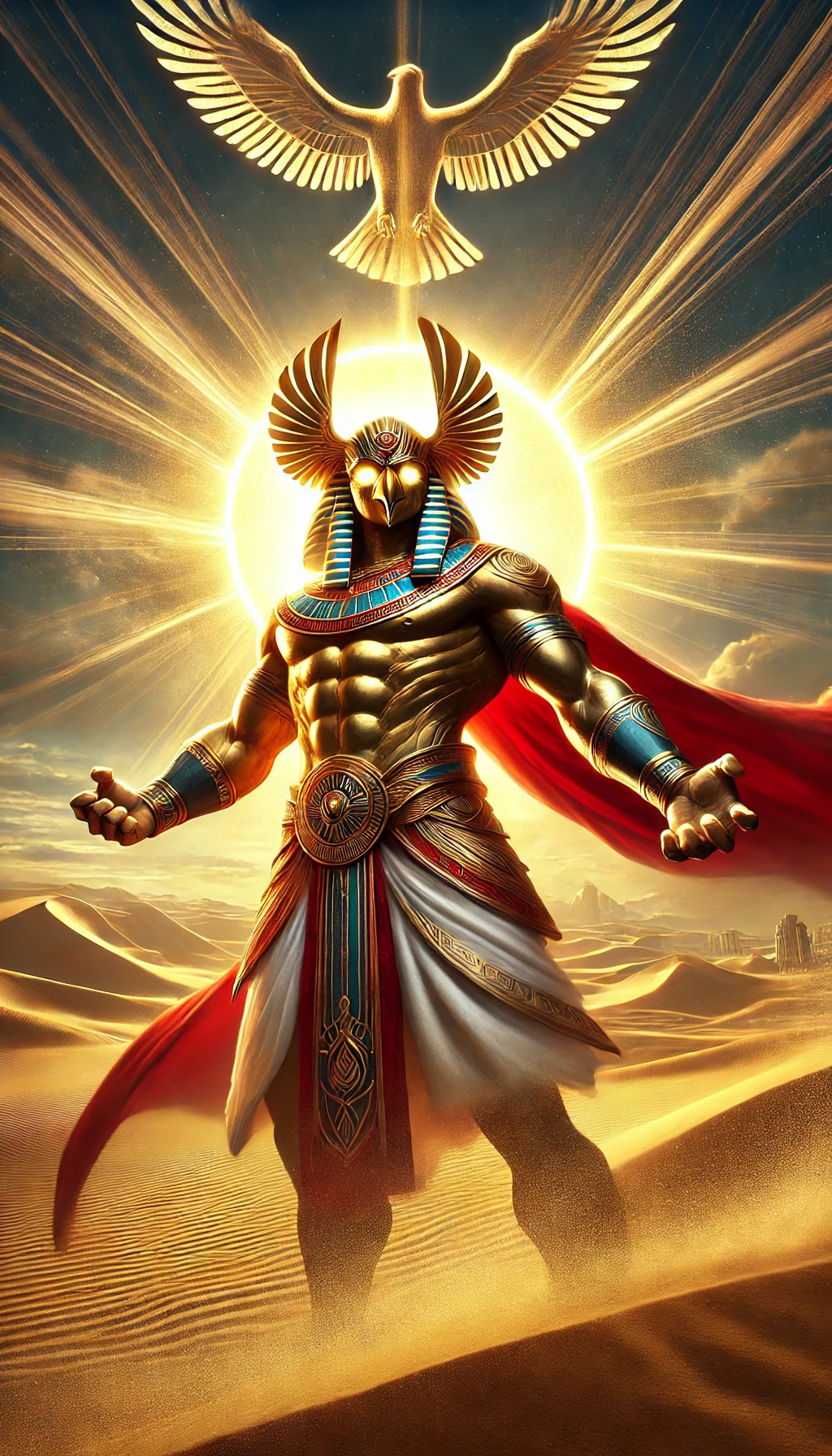

Clearly not as good as Midjourney, especially since it has a certain AI-ness to it that is easily identifiable these days. Most other programs don't have that, at least not to the same degree.
How Much Does Dall-E Cost?
Dall-E comes included with ChatGPT, although the number of images you're able to create will be potentially limited, depending on whether you have a free plan with ChatGPT or not. The ChatGPT Plus subscription will cost $20/month, but obviously comes with a lot more than just Dall-E.
Why I Don't Recommend Dall-E:
- Messier Images: while the accuracy of Dall-E is not bad, it lacks aesthetics. As you can tell by my litmus test image above, there's a sort of glossy look to it that isn't ideal.
You can access Dall-E via ChatGPT over at: https://chatgpt.com/
3. Stable Diffusion (via Leonardo.AI)
The last notable AI art generator is Stable Diffusion, an open source AI are generator that is easily the leader in open-source AI art generation.
Because Stable Diffusion is open source, there are a lot of different tools out there that use it. But the one that I recommend using is Leonardo.ai, which has a generous number of free credits that you can use each day to try it out, and then if you want to do more you can buy more.
Leonardo also has its own AI models, but lets you switch to various Stable Diffusion models, as well as fine-tuned models that are made by the community. So it's a versatile program.
You can also download Stable Diffusion onto your own computer, if you have a strong enough graphics card to handle it, and use it on your own. This is useful for people with highly technical backgrounds, because you can modify Stable Diffusion to work however you want. However, the instructions to do this are a bit more advanced, and beyond the scope of this article.
Here's what Leonardo was able to do with my litmus test.

Definitely not bad, though a bit cartoonish, and with a little tweaking, could easily get to the quality of Midjourney above.
How Much Does Stable Diffusion Cost?
Since Stable Diffusion is open source, it doesn't have a specific cost. Anyone can download it to their computer and run it for free.
However, doing so is highly technical and difficult, and you need a really good computer, such as a gaming computer, to be able to run it.
Therefore, most authors would be using an online service that uses Stable Diffusion as its base. And these can cost money.
I recommend Leonardo.AI, which has the following pricing tiers:
- Free – Gives you a generous 150 fast tokens/day
- $12/month – 8,500 fast tokens
- $30/month – 25,000 fast tokens
- $60/month – 60,000 fast tokens
Note that “tokens” are a measurement of GPU usage, and don't necessarily correlate to a single generation. Depending on the size of your image, or the type of model used, you could use more or less.
Also note that all tiers except the free version has privacy enabled, unlike Midjourney which only has privacy on the $60 or above tier.
So for pricing, Leonardo is even better than Midjourney, but there are still reasons why I recommend Midjourney overall…
Why I Still Recommend Midjourney Instead
Despite the fact that it is open source, there are several reasons why I would not recommend it to authors:
- Accuracy: in my experience so far, Stable Diffusion is not nearly as accurate as Midjourney, although it is getting much better, and many authors will not necessarily have needs that require the power of Midjourney.
- High learning curve: if you are downloading Stable Diffusion to use on your computer, there is an extremely high learning curve, and I only recommend it for those who know what they're doing. Even those using Leonardo have a lot more of a learning curve compared to Midjourney.
That said, if you're just interested in trying out some of the AI art generation tools out there, Leonardo is a good one to try, because you get a number of free generations every day, which is extremely useful.
You can access Stable Diffusion via Leonardo over at: https://leonardo.ai/
4. Ideogram
Last but not least, we have Ideogram, which is an interesting one. In some ways, it's not as good as Midjourney or the others, but in other ways, it's far better.
Let me explain.
While I don't know the specifics of how Ideogram was trained, it seems to excel at graphic design elements more so than illustrations and the like.
For instance, you'll see an example below of what it did when I asked it to create a fantasy author logo.
And while it doesn't do as well with my litmus test as Midjourney did (at least in terms of tone and aesthetics), it's not slouch there either.
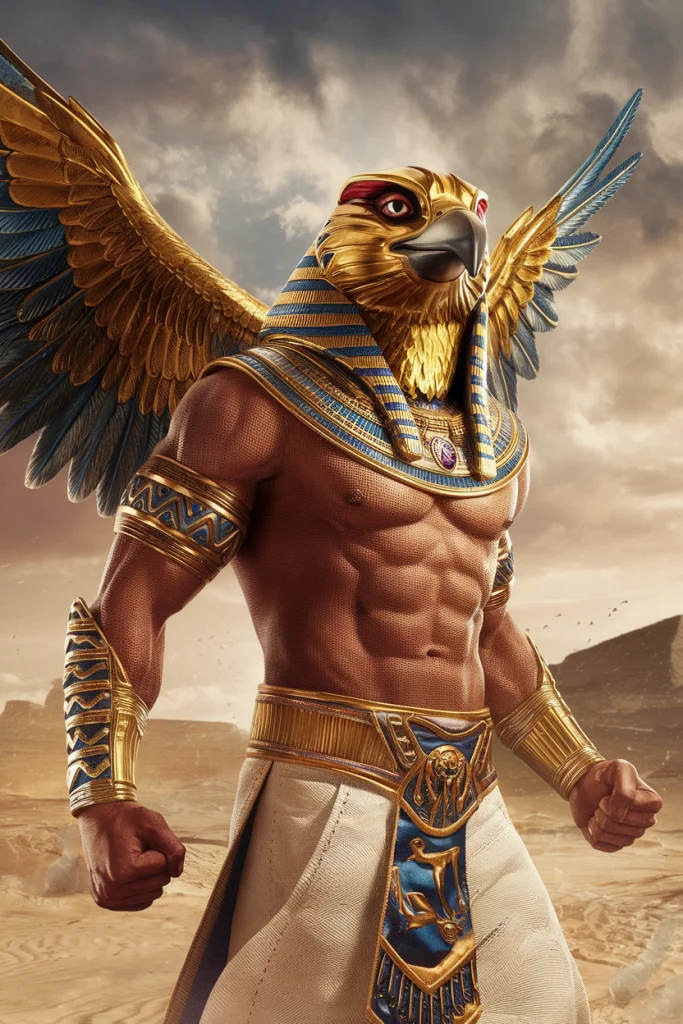

But what Ideogram really excels at, and the reason it's gained popularity among authors, is the fact that it's somehow really good at book covers. Moreso than any of the other models as of this writing, even Midjourney.
Here is an example of a book cover. Here is the prompt I gave it: Supernatural thriller novel book cover, the title is called “Shevan's Creek” and the author is “Author Name” with a subtitle of “A Supernatural Thriller Novel”

I don't know about you, but I'd probably buy that.
Additionally, if you'd like to know more about how to use Ideogram, I did a whole tutorial on it that you can find here:
If you want more videos like this talking about the practical uses of AI in writing and marketing, be sure to subscribe to the channel.
How Much Does Ideogram Cost?
Ideogram has the following pricing tiers:
- Free: 10 Slow Credits/week
- $8/month: 400 Priority Credits/month
- $20/month: 1000 Priority Credits/month
- $60/month: 3500 Priority Credits/month
There are a number of more advanced features, like being able to modify existing images and make them private that are only available on higher tiers.
You can access Ideogram over at: https://ideogram.ai/
What about AI Art Copyright?
But let's talk about the elephant in the room here: can you actually use this art? Is AI art stealing from artists across the Internet, and therefore is there legal protection granted to those creators?
For authors, we basically want to know if we're going to get sued.
Let's divide this into two issues:
- Commercial rights
- The legality of AI Art using copyrighted images
1. Commercial Rights
To answer this, let's first take a look at what Midjourney says. They say that “you own all Assets you create” but you also allow others to view, use, and remix those photos.
So basically, you have commercial rights to use those photos as you choose, but so does everyone else. In most countries, there are no rights granted to AI-generated art, so all images are essentially in the public domain.
Midjourney does offers a privacy plan, which keeps your images private. This means that no one else can see the images you produce. This makes it more difficult for others to use them, but not impossible, and they are still considered part of the public domain in most countries.
Now there is a limit to this. For example, if you generate a recognizable image of Batman, you could not commercially use that art, because you obviously aren’t the rights holder for Batman.
Likewise, it’s dangerous to use the likenesses of public figures in your AI art (although Midjourney does have a way of combining the likenesses of several people into one face that is fascinating).
Additionally, you can't copyright AI art without human modification (meaning you changed things about the image, arranged them in certain ways, etc.).
I made a whole video about this which you can check out here:
But what about the art styles of specific artists? Well, that leads us to the next question…
2. The Legality of AI Art
There are still a lot of lingering questions about the legality of AI art. As of this writing, there is very little legislation on this matter, although most of the court-cases that have come across these companies have been thrown out because the plaintiffs can't prove infringement (since the AI output would have to show significant similarity to any of the training material).
No doubt we will begin to see more laws take shape as legal action is taken against specific users or companies that generate AI art.
But for right now, the field is largely open.
However, there is a growing concern that AI art is simply copying from existing copyrighted material, especially in situations such as training the AI to mimic the style of an existing artist.
There's obviously nothing wrong with training the AI on a long-dead artist whose works are in the public domain, such as Leonardo da Vinci, but can the same be said for a modern artist who is trying to make a living today?
Format Beautiful Professional Books
Easy to use, and and full of amazing features, you can quickly turn your book into a professional book.
Check It OutThese are some of the questions that are as yet unanswered.
So far, most apologists for AI art agree that training the AI on someone's art is no different than how real humans work. We look at what exists, we try to mimic it, and put our own flavor on it. You can literally find entire college classes about how to mimic the style of other artists.
It's also worth pointing out that most AI art tools are not copying anything, they are learning.
Let me explain…
How AI Art Works
When AI is learning how to draw a cat, you feed it a lot of different pictures of cats. From this data, the AI is able to interpret the commonalities between all of the pictures of cats, helping it know the mathematics of what a cat should look like.
It can then re-create a picture of a cat in a variety of circumstances, but it is not actually copy/pasting from the pictures of cats that it has previously digested.
So to say the AI is copying from other people's work is tenuous at best. Even if it were copying, AI learns from millions of images across the Internet. In order to claim copyright infringement, you have to prove at least 10 percent of a given work was copied. In the case of AI art, the percentage is one in millions.
You can do this yourself, copy tiny pieces of various copyrighted artwork to create a collage. Collages are literally protected under copyright law, as long as you don't use more than 10% of a given work. (Note: AI art isn't actually making collages in the way it works, but if it were, that would still be legal).
I'm sure we will see more developing in this sphere, but this author is fairly certain that little will change. And from all of the intellectual property lawyers that I've read comment on this subject, there seems to be near-universal agreement that the use of copyrighted images in AI art is transformative, meaning it falls under fair use.
Will we see the definition of fair use change in the future? Possibly, but I wouldn't hold your breath.
As hard as it is for many artists and authors to accept, AI really is hear to stay. We have a much better chance of surviving by embracing the change instead of fighting it.
So with that in mind, what can we do with these tools that we couldn't do before?
Use Cases for Authors
Now it's time to get to the fun stuff: what we, as authors, can do to take advantage of AI art in our business.
If you have any additional suggestions, I would love to hear them, but so far this is what we’ve got:
1. Chapter Themes

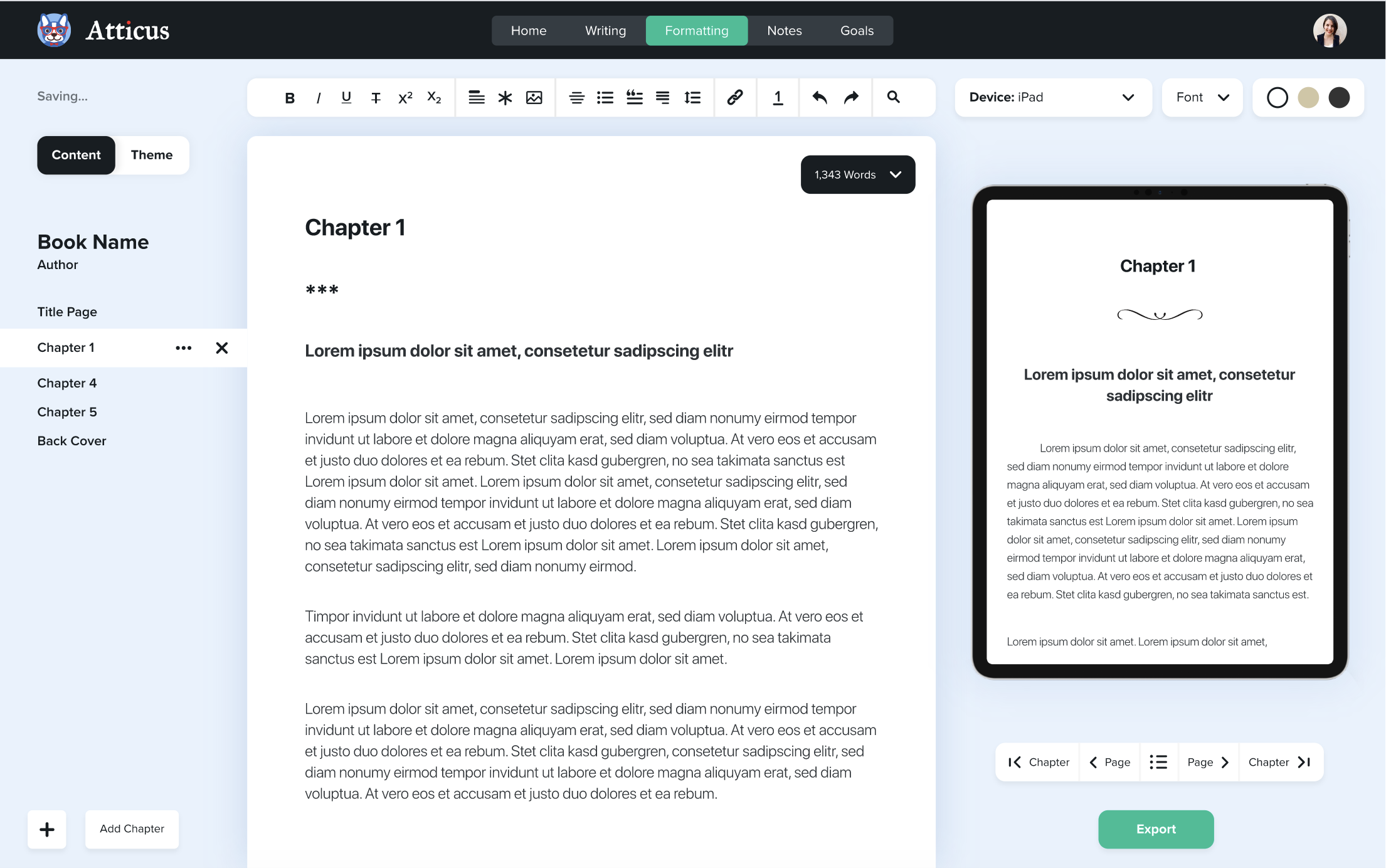
With a program like Atticus, you can create beautiful chapter themes for your book.
The problem that some authors run into, though, is that these chapter themes require art, and if the author is not also an artist, it can be really expensive to commission that art.
And so many chapter themes do not reach their full potential.
But with AI art, you can easily create images that you can use as full bleed backgrounds in your chapter theme, or full-page images, or smaller images that fit below your chapter title.
For this type of art, I recommend including in your prompts something like “charcoal art”, or “pencil art” which works better in a black and white interior of a book.
2. Concept Art

Even if future laws prevent us from commercially using AI art, one thing authors will no doubt be able to do is use AI art for concept art.
This can be a fantastic way to visualize your characters, creatures, locations, etc.
Plus, it's a great way to engage with fans by showing them the concept art of what you're working on. You can also use it as a guide for book cover designers to have an idea of what you're looking for.
As part of your concept art generation, I recommend using a prompt like “concept art”. You could also add a “white background” prompt if you want to see just your character, and nothing in the background.
3. Advertising/Marketing/Social Media

Another area that is ripe for AI art is all of the graphical images that you used to promote your books.
This can be anything from the photos you use in your advertising, to header images on your website, to social media posts.
You can even generate a lot of images to create TikTok or Instagram stories.
And if you are generating concept art, social media is a prime place to share it.
You could also use the images in certain types of YouTube videos. I personally follow a lot of lore-based YouTube channels, with videos that are glorified slideshows. This type of YouTube channel would be perfect for AI art.
I also personally use art very heavily on my website, MythBank.com, so that I can have high-quality images for each article I write, at a fraction of what it would cost me otherwise.
4. Pen Name Author Images

If you have a pen name, you might want to have a special image of your author profile.
In the past, authors would either do without an author photo for their pen name, or they would select a stock image.
The problem with stock images is that anyone can easily discover that it is not really an image of you. They can simply do a reverse search on Google Images, and find the stock photo.
But with AI art, you can generate unique, and realistic, photos of people that don't exist.
This makes it ideal to put a face on your author pen name.
5. Logos

While AI still struggles with text, it's actually getting pretty good at generating logos.
At the very least, you can run a prompt to generate a logo multiple times, get ideas, and send them to an actual illustrator.
But if you're in a financial bind, it's relatively easy to come up with a simple logo for your brand.
6. Book Covers
I will start this one with a warning: if it becomes illegal to use AI art wholesale, you are walking a dangerous line by creating a book cover out of AI art.
However, AI art can absolutely serve a function when creating book covers.
Consider this: most book covers are created by an artist using a program like Adobe Photoshop. What usually happens is the artist selects a number of stock photos, and skillfully manipulates them together into a single work of art.
For a skilled artist, they can create something truly unique, but you will often see the same stock model over and over in various book covers.
AI art would allow them to generate unique models and assets that could then be photoshopped into the book cover, just as stock photos are used now.
Additionally, you as the author could generate various ideas in AI art, then send them to your artist for inspiration.
In most cases, I would say AI art is not quite good enough to be used as a book cover without serious modification. At the very least, you need to add the text yourself, which is a whole different art form.
But there are still many exciting ways in which AI art can be used in book covers. For instance, I have used AI art for some of my book covers IF it's for a short story that I'm just sharing with my email list, and not planning on publishing on Amazon.
7. Comic Books and Children's Books

AI art still has a long way to come, and it is not yet to the point where you can create amazing comic book or children's book illustrations. Just getting the images to be consistent from panel to panel is a struggle.
However, there are already multiple cases of people generating entire comic books using AI art. See the above example, Zarya of the Dawn, which was the first known case of an author being granted a copyright over a comic book created with AI art (though the copyright was later rescinded, then re-granted).
Children's books are the same, and there are authors creating AI children's books as well.
How to Construct an AI Art Prompt
I've already established that Midjourney is, by far, my number one recommendation for creating AI art. And thankfully, constructing your prompt for Midjourney is very similar to how you'd do it in any other program.
But how do you actually generate these images? Is there a trick to making them look as good as you want them to?
Yes, as it turns out. Creating amazing images in any of these tools is something of an art itself.
Here are a few tips for writing great prompts to generate beautiful AI art.
Step 1: Start with the Main Subject
I always start my prompts with the main subject of the photo, usually a noun with just a few adjectives, and maybe a brief description of what the subject is doing.
In the case of my litmus test, this was simply “the Egyptian God Ra”, though it can be a little bit more complex if you need it to be, such as “an orange tabby cat wearing a spacesuit in space”.
Step 2: Keep It Simple
Try not to expect too much from AI art, at least not yet, because it still struggles with certain things.
Firstly, it is often hard to get two subjects to interact with each other. For example, if you entered a prompt such as “a woman riding a horse, with a man standing next to the horse, holding the reins”, the AI would likely struggle with this.
AI art is much better with single subjects, single actions, etc. Although it is getting better.
(This is assuming you want something specific out of your art. It can sometimes be even more fun to let Midjourney have its own creative take on something more vague.)
Step 3: Add A Few Modifiers
Once you have your main subject at the head of your prompt, you can then add a few additional modifiers, separating each with a comma. This is where I like to add specific details about the subject, the background, etc.
For example, in my litmus test, I added the following to my prompt: “head of a falcon, superhero pose, desert background”.
You can see here the difference between that prompt, and if I used a jungle background instead.

Step 4: Add Tones
After you have your main subject and your modifiers, I like to add a few words to specify the tone of the image.
For example, in my litmus test, I added the following to my prompt: “epic, powerful”.
You can see the difference between that prompt, and if I used a dark and gloomy tone instead.

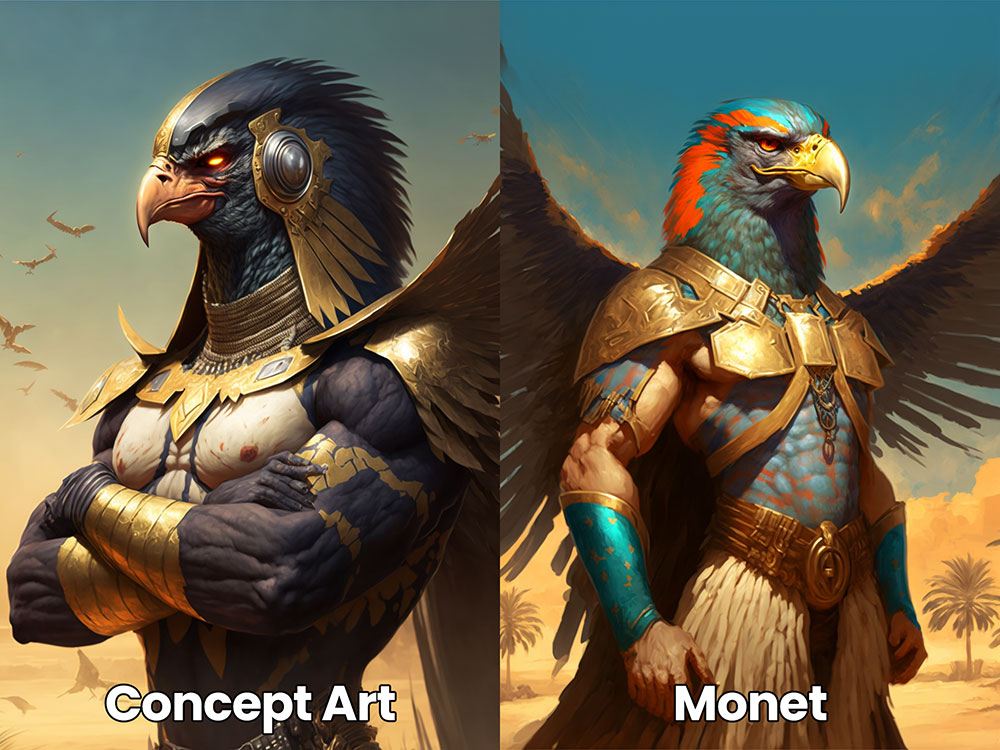
Step 5: Add Styles
At the end of my prompt, I will include the different styles that I want to evoke. This can be anything from a specific art style, to the style of a particular artist or photographer.
For example, in my litmus test, I put simply “concept art style”.
You can see the difference between that prompt, and if I used the style of Monet.

Step 6: Additional Commands
For Midjourney specifically, there are a variety of commands to improve your prompts. Here are some of the most common:
- –ar: This determines your aspect ratio of your image. By default, this ratio is squire (i.e. –ar 1:1). But you can create portrait or landscape images by imputing different numbers, such as –ar 16:9 or –ar 2:3.
- –stylize: Add this command to increase the stylization of your art. You can enter a number from 625 to 60000. Ex. –stylize 60000
- –quality: Add this command with a number between .25 and 5 to increase how long the AI spends working on your image. Ex. –quality 2
- –no: Add this command to remove a specific aspect from the image. Ex. –no green, or –no water
Note: Some of these commands might be limited in newer versions of Midjourney.
The above are just some of the most useful commands. For a complete list of commands, as well as a HUGE list of potential styles and techniques, I recommend visiting this GitHub page which has a lot of ideas.
How Far AI Art Has Come
2022 saw the explosion of AI art on the market. It had existed before this, but 2022 was the year that it finally became good enough, and affordable enough, for public consumption.
And given how fast these algorithms have improved, this rate of change has continued in the years since.
For example, just look at how much progress Midjourney made in 2022 alone:


As you can see, version 4 of Midjourney is vastly superior to anything that came before it.
And developments like this are what make AI art so exciting.
Because given how far the technology has come in just one year, I have no doubt that any issues the AI models struggle with will be resolved within the next 2-3 years.
Are You Excited Yet?
I truly believe that AI is one of the biggest revolutions to hit our society since the formation of the Internet, and AI art is one of the first tools to really shine and demonstrate the full potential of artificial intelligence.
As with any new technology, there will be growing pains, but history has taught us that often the people who embrace the new technology see great success moving forward.
Personally, I find AI art to be one of the most exciting opportunities in my career. It allows me, who couldn’t afford a lot of custom art otherwise, to create beautiful concept art for my books, stand-out chapter themes, and website artwork in no time.
I hope this article will help you get there as well.
And if you're interested in AI, I have a whole community where we study how authors can integrate AI into their businesses to enhance their career. We even have a dedicated graphic designer instructor, who will teach you about how to use AI art. You can find that community at this link: https://kindlepreneur.com/click/story-hacker